Drawing Of A Cell Wall
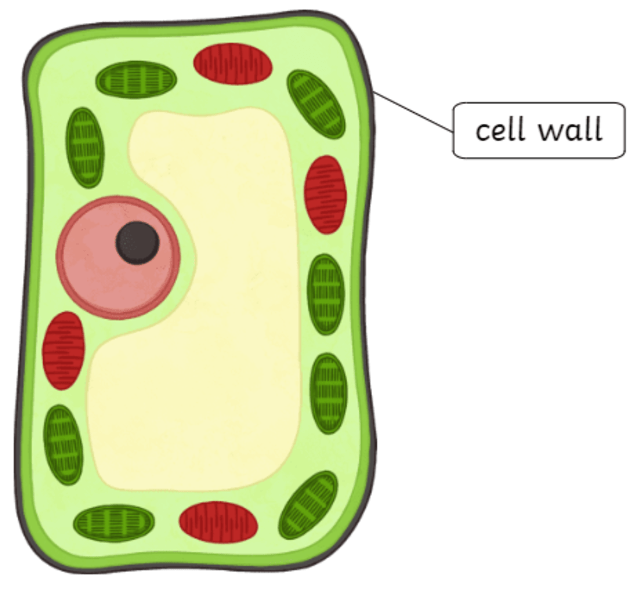
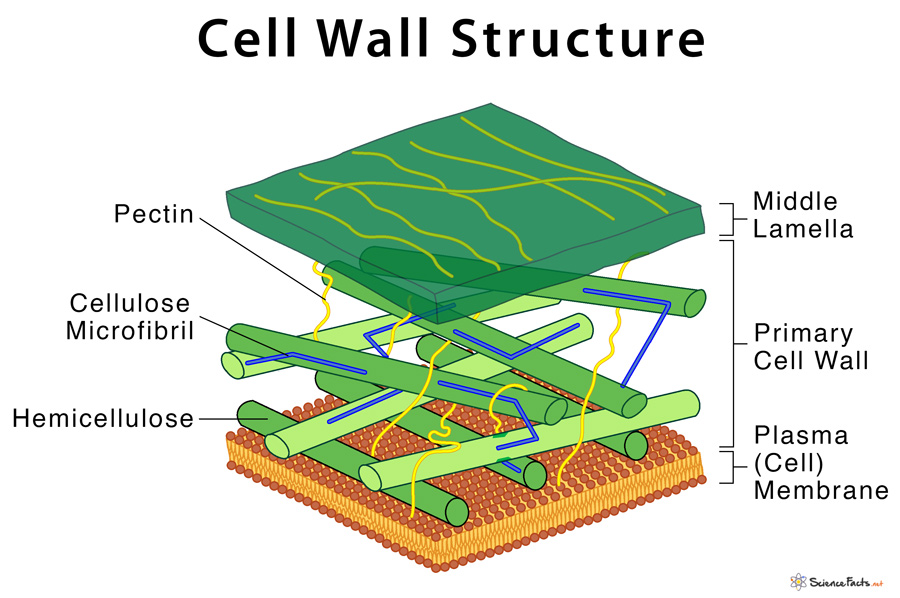
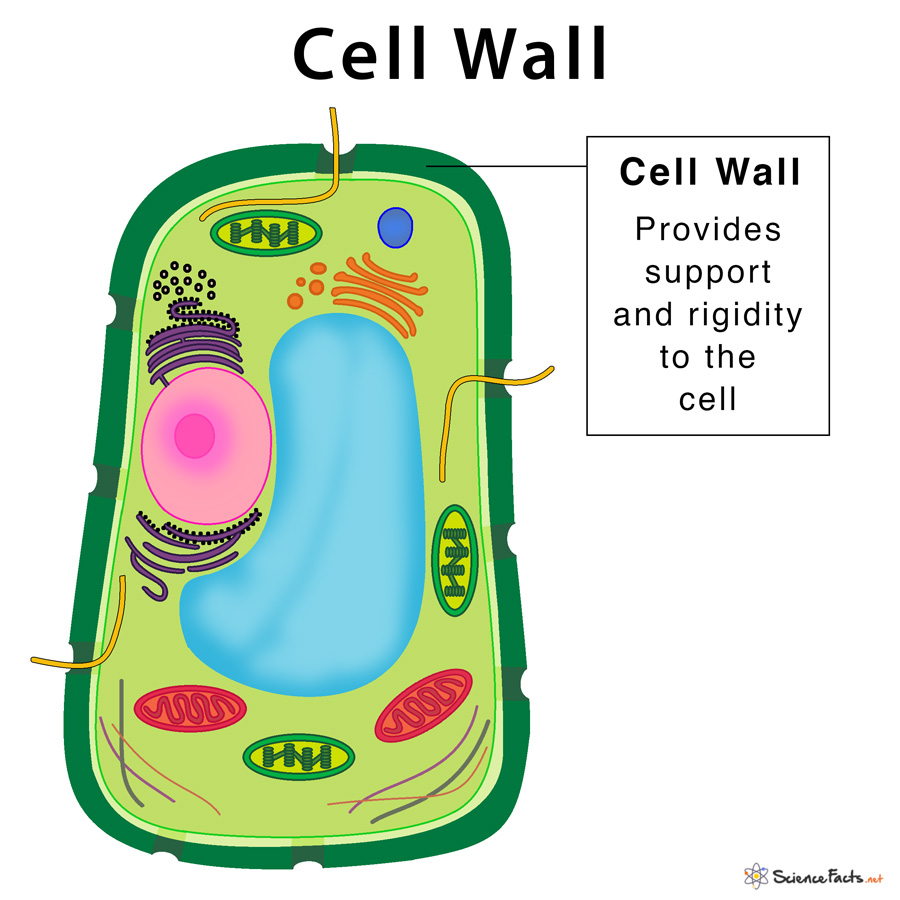
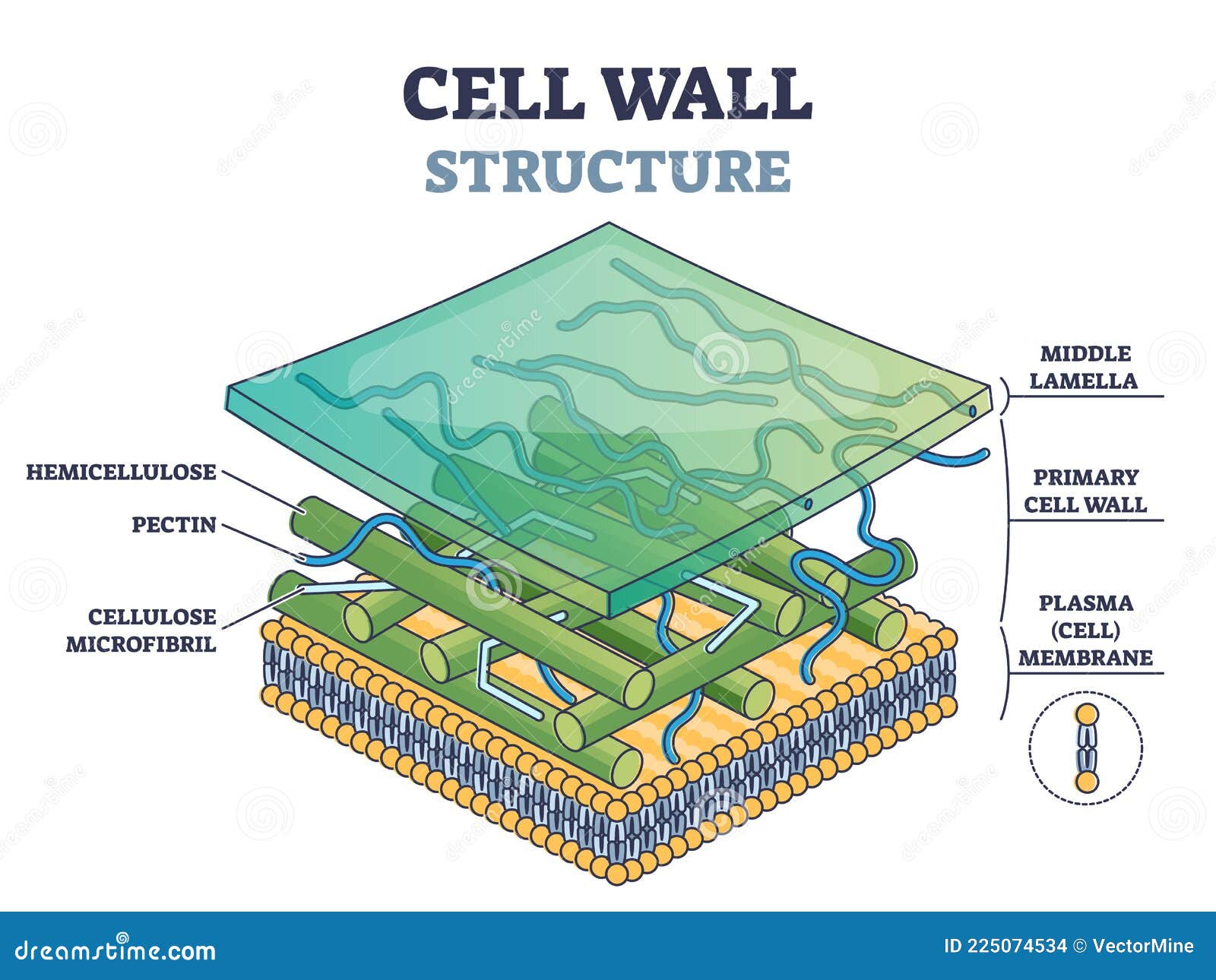
Drawing Of A Cell Wall - Cell structures and their functions. Unit 2 water, acids, and bases. Its outer coating is a semipermeable cell membrane. Primarily, it provides the cell with structural support, shape, protection, and functions as a selective barrier. Animal cells are the fundamental units of life in protozoa and multicellular animals. Providing the strength, structural support and maintaining the shape of the cell. Web a cell wall is a structural layer that surrounds some cell types, found immediately outside the cell membrane. The plasma membrane not only defines the borders of the cell, but also allows the cell to interact with its environment in a controlled way. Web an animal cell lacks a cell wall or chloroplasts. Cells contain parts called organelles. Cell wall was first seen in cork cells by hooke in 1665. Web the cell wall is a rigid covering that protects the cell, provides structural support, and gives shape to the cell. The cell wall is present in the plant cell and absent in the animal cell which distinguishes them from each other. Unit 6 structure of a cell. Web the primary cell wall is the first wall formed by the cell that gets deposited on either side of the middle lamella of the adjacent cells. Cell structures and their functions. This outer covering is positioned next to the cell membrane (plasma membrane) in most plant cells, fungi, bacteria, algae, and some archaea. Start practicing—and saving your progress—now: Plant cells connect directly to one another via tunnels in their cell walls called plasmodesmata. Cells must be able to exclude, take in, and excrete various substances, all in specific amounts. Cells contain parts called organelles. Unit 5 energy and enzymes. The plasma membrane not only defines the borders of the cell, but also allows the cell to interact with its environment in a controlled way. It is found in plants, algae, fungi, prokaryotes and eukaryotes. It is the outer rigid protective supportive and semi transparent covering of plant cells, fungi. Unit 9 more about membranes. The cell wall distinguishes plant cells from animal cells and provides physical support and protection. Web the main functions of the cell wall are: Web meaning of cell wall: Unit 8 membranes and transport. Web unit 1 intro to biology. Animal cells however, do not have a. Plant cells connect directly to one another via tunnels in their cell walls called plasmodesmata. In figure \(\pageindex{1}\), the diagram of a plant cell, you see a structure external to the plasma membrane which is the cell wall. The cell wall makes plants rigid and less flexible. It provides mechanical support and helps in maintaining the shape of the plant cell. Web an animal cell lacks a cell wall or chloroplasts. Its thickness varies in different types of cells from 0.1 µm to 10 µm. Cells contain parts called organelles. Unit 4 elements of life. Unit 4 elements of life. Web the cell wall is a rigid covering that protects the cell, provides structural support, and gives shape to the cell. All cells have cell membranes, but generally only plants, fungi, algae, most bacteria, and archaea have cells with cell walls. Web the cell wall separates the interior contents of the cell from the exterior. A cell wall is an outer layer surrounding certain cells that is outside of the cell membrane. Web a cell wall is a structural layer that surrounds some cell types, found immediately outside the cell membrane. It can be tough, flexible, and sometimes rigid. Web cell wall, specialized form of extracellular matrix that surrounds every cell of a plant. Web. Protecting the cell against physical damage and invading pathogens. Web the cell wall is a rigid covering that protects the cell, provides structural support, and gives shape to the cell. Web the main functions of the cell wall are: Web plants and fungi have a tough cell wall for protection and support, while animal cells can secrete materials into their. Providing the strength, structural support and maintaining the shape of the cell. Cell wall controls and regulates the direction of cell growth. A cell is like a whole city. Its thickness varies in different types of cells from 0.1 µm to 10 µm. Web courses on khan academy are always 100% free. Cells contain parts called organelles. Web the cell wall separates the interior contents of the cell from the exterior environment. It has a power plant, a post office, and even public transportation. Animal cells however, do not have a. Unit 2 water, acids, and bases. Web unit 1 intro to biology. All cells have cell membranes, but generally only plants, fungi, algae, most bacteria, and archaea have cells with cell walls. Cell structures and their functions. A cell is like a whole city. All cells have a cell membrane that separates the inside and the outside of the cell, and controls what goes in and. Unit 4 elements of life. The plasma membrane not only defines the borders of the cell, but also allows the cell to interact with its environment in a controlled way. Web meaning of cell wall: Cell wall was first seen in cork cells by hooke in 1665. Web cell wall, specialized form of extracellular matrix that surrounds every cell of a plant. Web the main functions of the cell wall are: Web cell wall definition. All cells have cell membranes, but generally only plants, fungi, algae, most bacteria, and archaea have cells with cell walls. Primarily, it provides the cell with structural support, shape, protection, and functions as a selective barrier. Web plants and fungi have a tough cell wall for protection and support, while animal cells can secrete materials into their surroundings to form a meshwork of macromolecules called the extracellular matrix. Plant cells connect directly to one another via tunnels in their cell walls called plasmodesmata. Web the cell wall surrounds the plant cell, providing both structure and protection. However, this cellular component is present exclusively in eukaryotic plants, fungi, and a. Unit 2 water, acids, and bases. Web the cell wall separates the interior contents of the cell from the exterior environment. Web what is a cell wall and what it does in a cell:Cell Wall Definition, Structure, & Functions with Diagram
101 Diagramss of a Cell 101 Diagrams
Cell Wall Definition, Structure & Function (with Diagram) Sciencing
cell wall Description, Properties, Components, & Communication
Simple Cell Wall Structure
Cell Wall Structure and Function
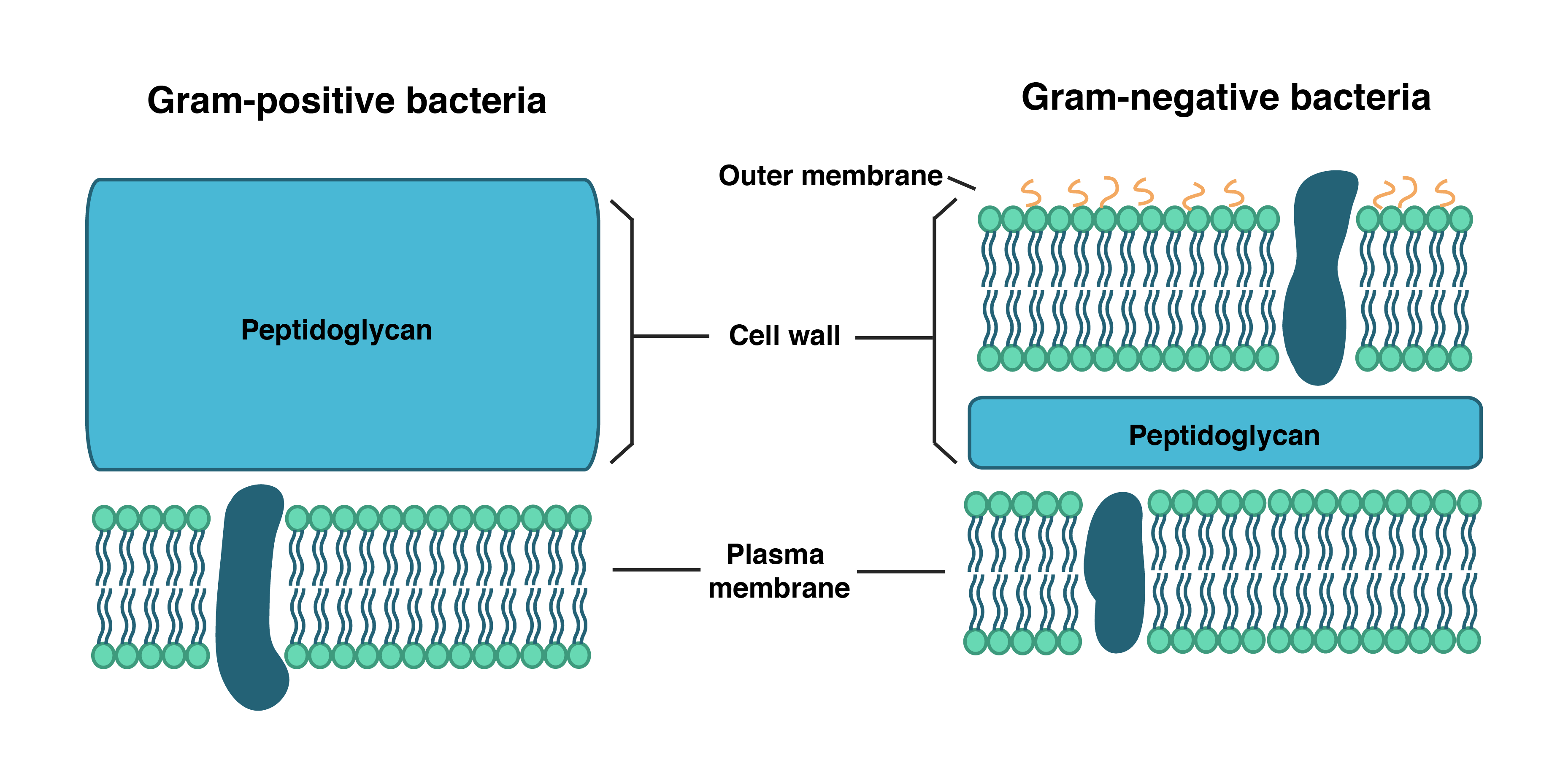
Prokaryotic Cell Wall Structure
Bacterial Cell wall Structure, Composition and Types Online Biology
What is a cell wall? Twinkl Teaching Wiki Twinkl
Plant Cell Wall Definition Structure Functions Diagram The Best Porn
The Cell Wall Is Present In The Plant Cell And Absent In The Animal Cell Which Distinguishes Them From Each Other.
Cell Walls Are Found In Both Prokaryotes And Eukaryotes, Although Not All Cells Have Cell Walls.
Web The Cell Wall Is A Rigid Covering That Protects The Cell, Provides Structural Support, And Gives Shape To The Cell.
It Is Found In Plants, Algae, Fungi, Prokaryotes And Eukaryotes.
Related Post:



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Plant_cell_wall_diagram-en.svg-58a8766c3df78c345bdc5df3.png)